Only a select few companies in the world offer both conventional and advanced inspection techniques.
Crestone NDT IS ONE OF THEM.
the two primary nde inspection techniques -
Saturated Low Frequency Eddy Current( SLOFEC ®)
-- Advanced inspection technique used when coating is involved, including fiberglass and rubber.
Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
-- Conventional technique of inspection usually used in no coating situations.
slide to read more on these techniques
SLOFEC
MFL
what is slofec
The SLOFEC™ (saturated low frequency eddy current) inspection system is based on the eddy current principle with superimposed DC field magnetization.
With this system objects with up to 25 mm wall thickness and coating up to 10 mm are testable, depending on the scanner type.
The task of the inspection system is to detect defects in tank floors, walls and roofs as well as in pipe walls. Due to the phase spread between subsurface (outside), surface (inside) and other indications the SLOFEC™ Operator is able to distinguish them from each other. Objects with non-conductive and non-magnetic coating, like rubber or paint, are also testable. A special coupling medium is not necessary.
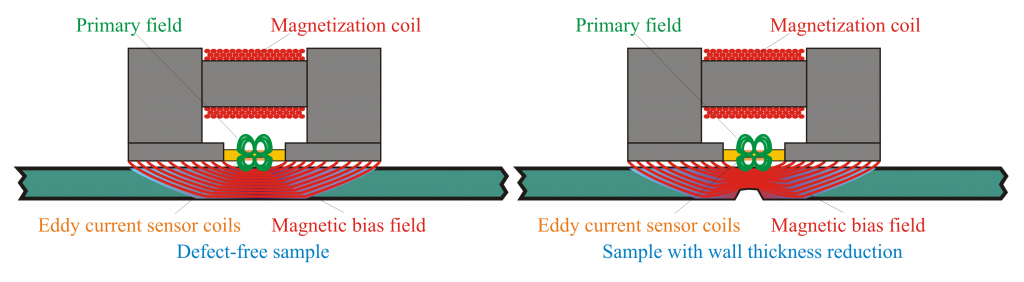
The figure schematically shows the working principle of the SLOFEC® technique. A magnetic yoke containing a permanent or electro-magnet is used to generate a strong magnetic field in the material to be tested. The magnetic DC field has an effect to the material properties of the test sample.
Between the poles of the yoke an eddy current sensor array is located. These sensors also generate a small alternating magnetic field in the material under test, super-imposed to the magnetic bias field of the yoke. The eddy current field is sensitive to changes of the material properties of the test sample. In a defect-free sample the magnetic bias field and therefore the material properties do not change. As a result the eddy current signal is unchanged.
A reduction of the wall thickness, e.g. by a corrosion pit will result in a concentration of the magnetic fields in the remaining wall and resulting in an increased magnetic field strength above and around the defect. This results in a Change of the material properties at this location. This local change of the material properties will be detected by the eddy current sensor.
The eddy current signal amplitude of the defect indication is a measure for the volume of metal loss.
what is mfl?
Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) inspection is a method of NDT used to detect and assess corrosion, pitting and wall loss in lined and unlined metallic storage tanks and pipelines.
Magnetic flux is the product of the average magnetic field times the perpendicular area that it penetrates. It is a quantity of convenience in the statement of Faraday’s Law and in the discussion of objects like transformers and solenoids.
In tank floor inspection, the floor of the tank is swept with the MFL tool. The area is flooded with magnetic flux and rare earth magnets are used to temporarily magnetize the steel while the magnetic field changes are recorded and analyzed. If the magnetic field is uniform, there are no flaws in the tank floor. If the magnetic field is distorted, internal or external flaws are present, such as pitting or corrosion and this distortion or “leakage” can be measured by the sensors.
Technicians proceed to mark areas that need to be verified by visual and ultrasonic inspections. The results obtained from the MFL inspection can be reported and used to establish an existing baseline for the equipment or to determine remaining wall and fit-for-service corrosion calculations in accordance with API, EEMUA and other applicable standards.
